
Adacel ® Vaccine is a combination vaccine that helps protect against three different infectious diseases - diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis. Adacel ® Vaccine is used for booster vaccination against these three diseases. Diphtheria, pertussis, and tetanus are diseases, which can be easily prevented with the help of vaccination*.

ADACEL® [Tetanus Toxoid, Reduced Diphtheria Toxoid and Acellular Pertussis Vaccine Adsorbed], is a sterile, uniform, cloudy, white suspension of tetanus and diphtheria toxoids adsorbed separately on aluminum phosphate, combined with acellular pertussis vaccine and suspended in water for injection.ADACEL® is indicated for active booster immunization for the prevention of tetanus, diphtheria and pertussis (whooping cough) as a single dose in persons aged 11 to 54 years*.
Immunity against diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis decreases steadily within 5 to 10 years after vaccination 1-3*
*Regardless of pertussis vaccine given during childhood (whole-cell pertussis or cellular pertussis).
While vaccines are effective, typically the level of protection gradually decreases over time.4
Similarly, protection conferred by natural infection also wanes with time.
Given the success of existing primary vaccination campaigns in children, the amount of
circulating disease which causes natural boosting of immunity has declined.5
This, coupled with the waning immunity acquired from childhood vaccinations,
can result in older children, adolescents and adults becoming:6-9
Vaccination against diphtheria,tetanus and pertuss is remains the single most effective strategy to prevent infection from these bacteria.10 Primary vaccination does not provide enduring protection.1
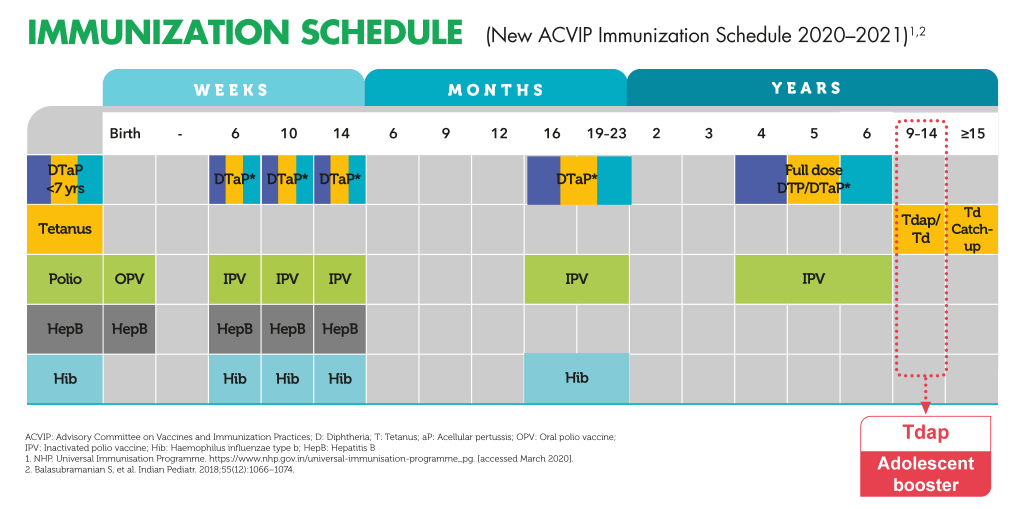
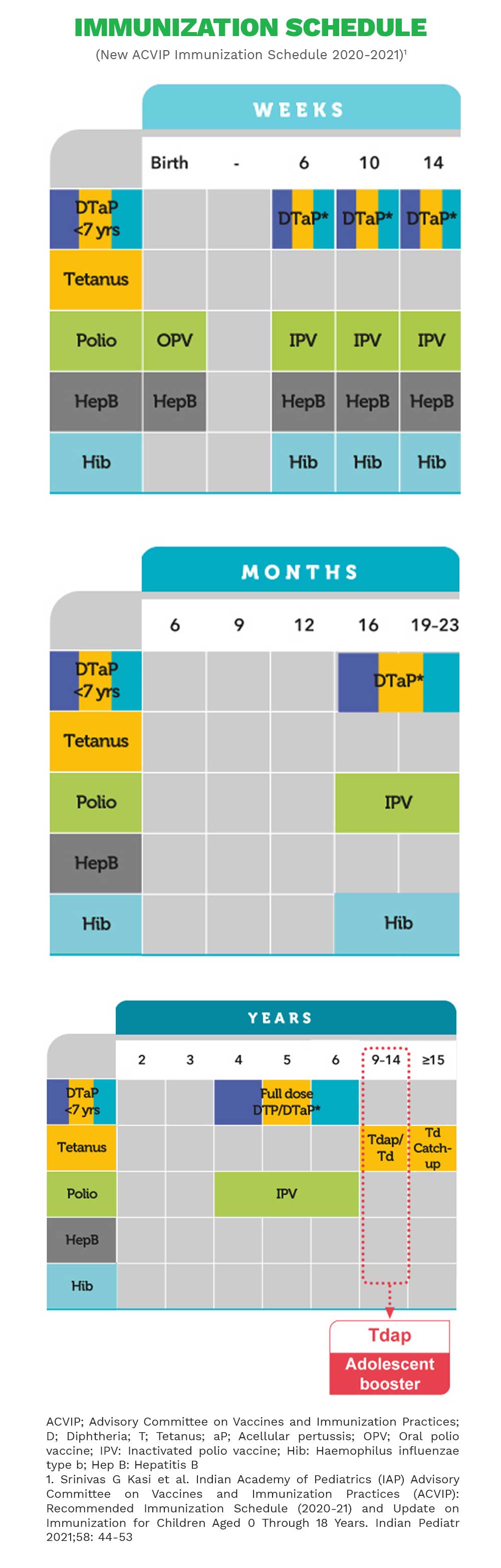
References:1.Liang JL,et al.MMWR Recomm Rep.2018;67(2):1-44. 2.Forsyth KD,et al.Cl in Infect Dis.2004;39(12):1802-1809. 3.Pool V,et al.Vaccine.2018;36(17):2282-2287. 4.Arlant LH,et al.Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther.2014;12(10):1265-1275. 5.ChiappiniE,et al.BMC Infect Dis.2013;13:151. 6.Jané M,et al.Euro Surveill.2018;23(13):17-00183. 7.Forsyth KD,et al.Vaccine.2018;36(48):7270-7275. 8.Hewlett EL,et al.N Engl J Med.2005;352:1215-1222. 9.Zhang L,et al.Cochrane Database Syst Rev.2014(9):CD001478. 10.CDC.MMWR.2012;61(28):517-522.